As a product moves uphill from the manufacturing stage to the selling point, it consistently sees an increase in its value. Once it has been purchased by the end-consumer the product’s value is at its highest. However, when the product’s usability ceases it gradually moves downhill and its value begins to decrease at every step. This is the traditional lifespan of a product on the value hill. Its’ value is determined by its core benefits but only for a certain period of time. The Value Hill Business Model expands on this idea.
What is the Value Hill Business Model?
Value within a company’s business model can be defined in three ways:
- Create Value – The company persuades customers to be willing to pay for the offered value
- Deliver Value – The company actually makes the offered value into a reality
- Capture Value – The company converts payments to profits.
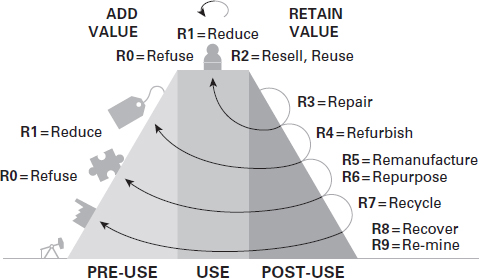
The Value Hill is a strategy framework that equips businesses with the right concepts to position their business, their strategy and their value chain in a circular context. * As you can see from the figure below that the Value Hill is an actual hill with an ascending and a descending movement.
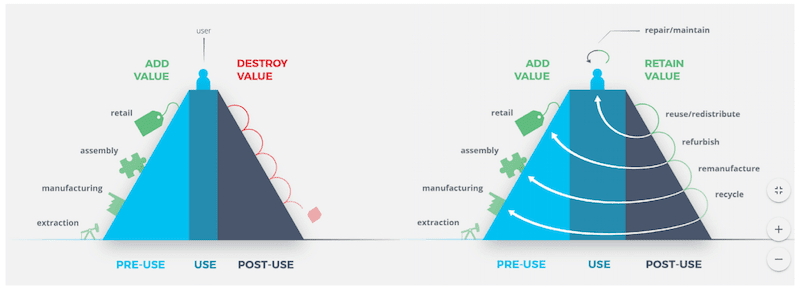
The Value Hill focuses on 3 phases – pre-use, use, and post-use.
What is the concept of the Value Hill?
The Value Hill divides the product’s lifespan into three phases:
- Pre-use, which is when the product begins its’ ascend up the hill. This is the phase where the product undergoes extraction, manufacturing, assembly, and value is added to the product at every step of the climb.
- The product receives maximum value when it is purchased by a consumer and it enters the use phase. This is where the product is consumed for its utility.
- Once the product has been entirely utilized, it begins its’ descend downhill. In this post-use phase, the product loses its value as it is no longer of use to the consumer.
A circular strategy strives to slowing the loop on the post-use phase and keep the product at its highest value for as long as possible. While the product is kept at highest maintenance during its upward journey or even when it reaches its highest value, the product’s component and materials can be taken back to the previous stage – on the left side of the Value Hill. This way the product enters a reusing phase where its value is not lost but retained. When the product’s lifecycle finally comes to an end, the loop is closed by recycling its remaining parts to create new value.
Climbing the R-Ladder with Value Hill
To add maximum value to a product and keep it at the zenith of the Value Hill, a company needs to ensure that its strategies are high up the R-ladder
The R-ladder is the degree of circularity which states that higher a strategy is up the ladder, the more circular it is. ** The figure below shows the R-ladder.
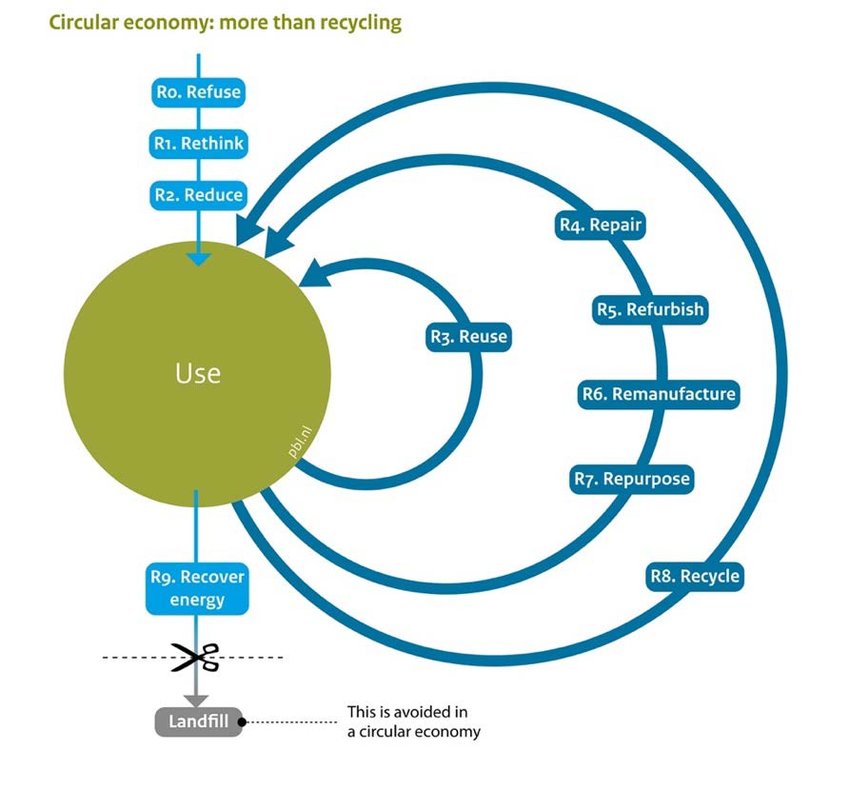
Each R strategy has a different implication for use, design, manufacturing, consumer, and an afterlife stage. There are overall 10 strategies that start with R and they can be divided into 3 stages in the Value Hill:
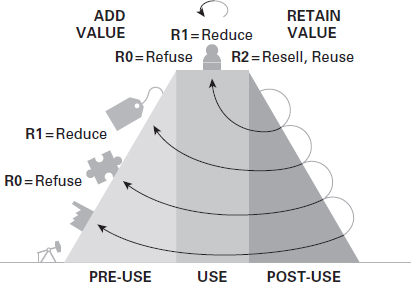
Stage 1: Refuse, reduce, and resell/reuse
This strategy aims to refuse disposal or waste of raw materials after its utility and reduce significantly the use of hazardous materials and chemicals at the design stage. It encourages the switch to mono-materials or the use of secondary raw materials to eliminate waste and pollution. It entails the reuse or reselling of products as a whole, almost for the same function or with little to no need for adaptation by another purpose.
Stage 2: Repair, refurbish, and remanufacture & repurpose
This stage aims to expand the lifespan of the product. Instead of disposing and replacing the product, it tries to create a culture of return and reuse by leveraging heavily on repairing the product. It maximizes product utilization to avoid any waste.
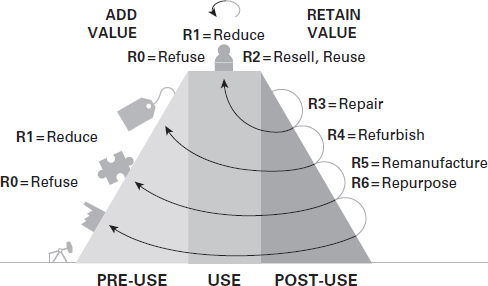
Stage 3: Recycle, Recover, and re-mine
The most ideal concept of circular economy is that the entire product including all its components and materials must be reused. Even when this isn’t always possible, the product’s components and materials must be reusable.
The Value Hill Business Model is a shift in strategy where businesses strive to focus more on quality than quantity. It helps companies understand how they can position their business in a circular context and contribute to developing a more circular economy. It also encourages businesses to have more control over their resources and preserve a product at the highest value to optimize its residual value.
Want to know more?
The Blue Connection, an innovative web-based business simulation game, is modeled around circularity and gives the participant the scope to learn by doing. It engages participants in the transformation from a linear to a circular value chain by implementing a circular strategy for a virtual e-bike manufacturer. In teams of 4, participants will represent the functional roles of VP Finance, VP Purchasing, VP Supply Chain, and VP Sales. Experience the circular way of doing business for a sustainable future!
 Now you know
Now you know
Now you know that the Value Hill model can be defined by creating, delivering, and capturing value. The Value Hill in fact looks like an actual hill. It divides the product’s lifespan into three phases. Firstly, the pre-use phase where the product is being manufactured and distributed to markets. At this phase, as the product ascends uphill it gains value at every stage. Secondly, the use phase is when the product’s value is at its highest. Here the product reached maximum utility in the hands of the consumer. Thirdly, the post-use phase is when the product is no longer of utility to the consumer. It gradually moves down the hill and with every step the product begins to lose its value. The Value hill business model strategy tries to create a loop in this post-use phase and keep the product at its highest value for as long as possible.
Sources
- Ed Weenk's 'Mastering Circular Economy'
https://bookshelf.vitalsource.com/reader/books/9781398602762/epubcfi/6/42[%3Bvnd.vst.idref%3Dch020]!/4/2[ch04_sec_001]/32/1:547[ng%20%2Cmax] - Mastering Circular Business with Value Hill
https://www.circle-economy.com/news/master-circular-business-with-the-value-hill - Value in a Linear Economy
https://guides.co/g/value-hill/190711
You might want to learn more about

The Blue Connection
The Blue Connection is an innovative web-based business simulation game. It engages participants in the transformation from a linear to a circular value chain by implementing a circular strategy for a virtual e-bike manufacturer. In teams of 4, participants will represent the functional roles of VP Finance, VP Purchasing, VP Supply Chain, and VP Sales. Experience the circular way of doing business for a sustainable future!
Dive into our
knowledge base
Alignment
Blended learning
Experiential learning
Learning
Supply chain
Sustainability
- Sustainability
- Carbon footprint
- Circular Economy
- Does Green Governance drive the ride to a sustainable future?
- Everything You Need To Know About Eco-Efficiency
- Greenwashing: Everything you need to know
- Is it possible to measure the Triple Bottom Line?
- Sustainability v/s Circularity
- The 3Ps Series: People
- The 3Ps Series: Planet
- The 3Ps Series: Prosperity
- The Butterfly Diagram
- The Value Hill
- What are the 3Ps of Sustainability?
- What do we know about the Triple Bottom Line?


